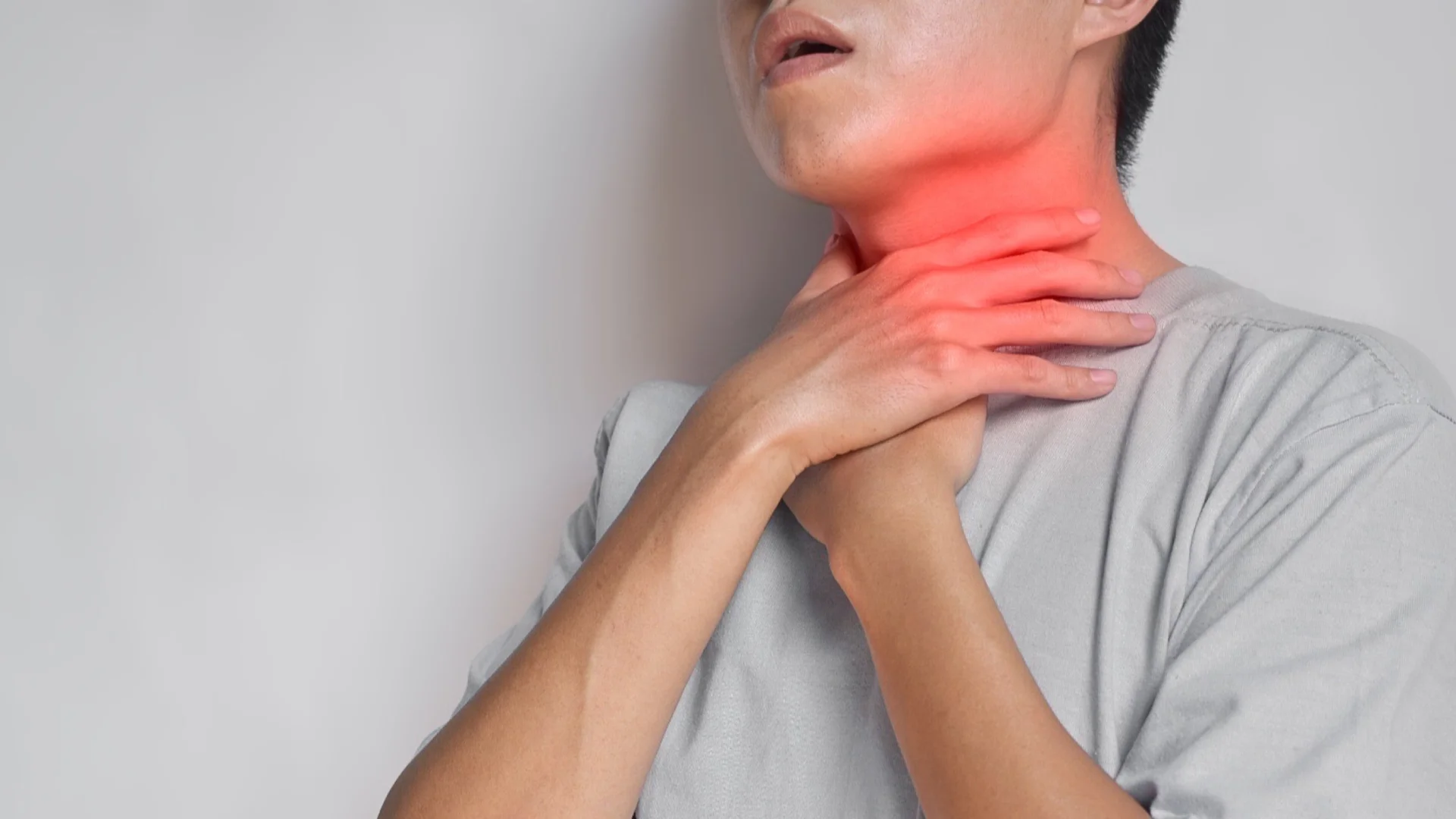
What You Need to Know About Dysphagia ✨
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is more than just an inconvenience—it can be a sign of something serious, especially if you're over the age of 45. While it can occur at any age, it’s essential to address it promptly to rule out potential causes like esophageal cancer or other health issues.
What Causes Dysphagia? 🔍
There are many reasons why swallowing might become difficult, including:
What are the Symptoms of Dysphagia? 🤔
Difficulty swallowing often comes with other symptoms, such as:
How is Dysphagia Diagnosed? 🩺
If you’re experiencing dysphagia, your doctor will likely start with a thorough examination of your mouth and throat. They may recommend additional tests, including:
How Can You Prevent Dysphagia? 🛡️
Some simple lifestyle habits can reduce your risk of developing swallowing difficulties:
Final Thoughts 💡
Dysphagia might seem like a minor inconvenience, but it’s often a symptom of a bigger problem that deserves attention. If you’re experiencing swallowing difficulties, don’t wait—schedule a consultation with a specialist. Early detection and treatment can help keep you comfortable and healthy!
🩺 Explore out our Check-Up Programs!
DISCLAIMER: The information presented on this page has been intentionally condensed and simplified to make it accessible and easier to understand for the general audience. Its purpose is solely to provide basic awareness and education on the topic discussed. It is important to note that this content is not exhaustive and does not replace or serve as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Readers are strongly advised to seek consultations with qualified healthcare professionals or specialists for accurate assessment, personalized guidance, and appropriate medical care. Relying solely on the information provided here, without professional oversight, may lead to misunderstandings or inadequate treatment.
Privacy policy
Copyright ©2025 Klinika Kajo. Designed By Vizional